Institute Facilities
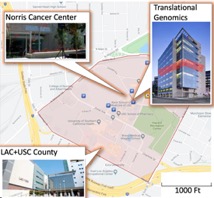

Other important components are The Los Angeles County Hospital, called LAC+USC Medical Center, which is one of the largest public academic medical centers in the country and a disproportionate share hospital (DSH) dedicated to the underserved. Just a 5-minute walk from USC Norris headquarters where Dr. Lynda Roman lead the division of Gynecologic Oncology where multiethnic patients attend the endometrial cancer clinic which is potentially recruited for the Gynecologic Tissue and Fluid Repository (GTFR) team lead by Dr. Roman.


The Norris Headquarters Building. The USC/Norris Comprehensive Cancer Center is headquartered in a nine-story 171,400 gross square feet (95,100 net assignable square feet) building, which was opened in 1983 and was the first facility of its size in the Pacific Southwest designed and built solely for the purpose of conducting basic and clinical cancer research programs. This building was expanded in 1994 by the addition of 5,000 nsf (included in the figures above) to the Radiation Oncology Department.
The Topping Tower. The Topping Tower addition to the Norris building is contiguous to the existing building at the ground, first and second floors and connected by a bridge at the fifth floor. Areas of the existing ground, first and second floors were extensively remodeled to accommodate new or relocated functions. The Topping Tower was occupied in 1996, and the renovations in the Norris building completed by mid-1997. It provides approximately 100,000 nsf of space and houses the following components: outpatient clinics and day hospital, clinical pathology laboratories, research laboratories, academic offices, research support space and conference facilities.
Harlyne Norris Translational Research Tower. An exciting development at our Cancer Center is the completion of the 172,400 gross sq. ft. Harlyne Norris Translational Research Tower. This $94 million building provides us with approximately 100,000 sq. ft. of assignable space and houses the Aresty Conference Center, which has facilities for about 200 attendees. The new building, is connected directly to the existing two buildings and has space for an expanded CISO office, provides two new floors of research space for molecular epidemiology and five floors of wet lab space for basic and translational research. Recruitments for new Cancer Center faculty who will fill this space have begun. Plans are to recruit 30-40 new investigators into the Cancer Center and the initial six recruitees have already begun work in this new research space. The building is financed entirely by University debt, which is secured to some extent by $47 million of capital, which we have raised from philanthropy. The University has agreed that the Cancer Center will have access to the interest generated from the $47 million capital sequestration.
Cancer Research Laboratories (CRL). This two-story structure of 11,800 nsf is owned by the County of Los Angeles but was built with the aid of the NCI construction grant awarded in 1973 to the then LAC+USC Comprehensive Cancer Center. The facility was occupied in 1976 and is managed by the School of Medicine through the Cancer Center Director. The building contains nine laboratories of 900 square feet each, plus shared areas such as cold rooms, instrument rooms, centralized glassware washing, darkroom and counting room. One-third of the first floor is devoted to vivaria, including animal procedure rooms, transplant room, cage washing and autoclaving, and a clean area to house nude mice.
Norris Hospital Facility. Currently, the Norris Headquarters Building houses 60 inpatient beds and outpatient facilities for cancer care. The University owns the buildings, which house the clinical activities; however, the hospital and outpatient businesses are now owned and operated by Tenet Healthcare Corporation. Tenet Healthcare is currently constructing a 10-story addition to the University Hospital one block from the current Norris facility which will house 70 cancer beds in the new Norris Tower. The plan is to move the existing beds to the new facility and utilize the space created by this movement to expand the outpatient facilities within the Cancer Center. The purchase of the Norris Hospital business by a for-profit hospital operator was approved by the Attorney General of the State of California following detailed and extensive negotiations. Several safeguards have been incorporated into the agreement, which will guarantee that the Cancer Center’s research mission can be fulfilled. Included in these are a process by which the Cancer Center Director and Chief Operating Office of the Norris Hospital can deal with potential conflicts. If there is significant disagreement, which cannot be resolved, the disputes can be taken to the Hospital Board for resolution. The Cancer Center Director sits on the Norris Hospital Governing Board and has the sole authority to nominate the Medical Director who is responsible for the oncological services conducted in the hospitals and clinics. Additionally, the Chief Executive Officer and Chief Operating Officer of the University Hospital and the Norris Hospital sit on the USC/Norris Comprehensive Cancer Center Advisory Board allowing feedback from that advisory board on the quality and direction in which the clinical services are evolving. This arrangement was presented on two occasions to our External Advisory Committee and to the NCI who endorsed the safeguards we have implemented to ensure that the Cancer Center’s research mission can be maintained and will flourish.
The Department of Translational Genomics (DTG) was established at KSOM in January 2016 under the direction and vision of inaugural chair, John D. Carpten PhD, and Vice Chair Dr. David Craig PhD. The current Department (Founded January 2016) consists of a highly collaborative and productive set of six faculty members including, John Carpten (Chair), David Craig (Vice Chair), Zarko Manojlovic PhD, Troy McEachron PhD, Bodour Salhia PhD, and Enrique Valezquez MD PhD. Four of the six are also members of the NCCC.
The Southern California Clinical and Translational Science Institute (SC CTSI)


- The SC CTSI Clinical Research Support group provides expertise and physical infrastructure for the conduct of early phase clinical trials and human mechanistic studies as well as comprehensive services for the design, conduct and reporting of clinical trials (biostatistics, research coordinator pool, participant recruitment, regulatory support, voucher program, auditing and monitoring, scientific review). This group also works to streamline the clinical research process.
- The SC CTSI Community Engagement group develops academic-community partnerships to help set research priorities, support community partnered research projects and programs, and disseminates research findings to the community.
- The SC CTSI Clinical Research Informatics group provides access to clinical information for clinical research as well as support for planning and conduct of data acquisition, management and analysis. A main thrust of current activities is provision of access to EHRs at three main partners, USC, Children’s Hospital Los Angeles, and Los Angeles Department of Health Services. The Informatics group also offers free access to REDCap, a CTSA consortium product that provides user-friendly data acquisition and storage.
- The SC CTSI Workforce Development group provides live and web-based training in clinical and translational research and funds career development of clinical researchers. The centerpiece of this group is a Mentored Career Development (KL2) program that enrolls four clinically trained junior faculty members each year into a 3-year program designed to prepare them for individual careers in clinical and translational research. Workforce Development also sponsors mentor matching and training in clinical and translational research.
- The SC CTSI Digital Innovation and Communication group develops novel digital solutions for challenges in clinical research, such as participant recruitment, dissemination of results and digital scholarship.
- The SC CTSI Research Development group identifies research priorities, community health needs, and challenges in the clinical and translational research process and develops and supports research teams to address those priorities, needs and challenges. The research development group also conducts and supports research on team science.
- The SC CSTI Evaluation and Improvement group helps the SC CTSI set goals, objectives and metrics; collects, analyzes and reports data on productivity and impact; and works with SC CTSI leaders to improve processes, quality and productivity of the Institute. Main thrusts of this group in the current grant cycle are accrual to clinical trials, careers and productivity of KL2 scholars, and IRB efficiency.
SC CTSI resources are available to all faculty members at USC and to researchers at other institutions in the SC CTSI partnership. Resources are provided on the basis of scientific merit, translational potential and match with the CTSI’s emphasis on clinical and community research, streamlining of the clinical research process, and development of a skilled workforce for clinical and translational research.
National CTSI Programs: The SC CTSI participates in several programs, sponsored by the National CTSA Consortium, that benefit research being conducted at USC and CHLA. Research Match is a national research volunteer registry that brings together researchers and volunteers who want to get involved in research studies. The Trial Innovation Network is a network of CTSI hubs linked by regional coordinating centers (Trial Innovation and Recruitment Innovation Centers) which together provide infrastructure for development and conduct of multicenter clinical trials. The SMART IRB Exchange provides infrastructure for facile multi-site reliance on a single IRB for multicenter trials. The Accrual to Clinical Trials (ACT) Network is NCATS’ nationwide network of CTSA hubs that share EHR data to significantly increase participant accrual to the nation’s highest priority clinical trials
Clinical Trials Unit – HSC: The CTSI operates a Clinical Trials Unit (CTU) located in Keck Hospital on the USC campus, adjacent to the PIs office and lab. The CTU has exam rooms, infusion rooms, and study coordination for junior investigators, blood draws, blood processing, medication administration, subject monitoring, specimen processing and/or shipping, IV administrations for infusion therapies, EKGs, spirometry, statistical analysis consultation, telemedicine video conferencing, database design and creation, data storage services. Junior faculty have high priority for use of the facility. CTSI also provides biostatistical support for study design, data acquisition and management, and data analysis; pilot awards; and training and career development support.
Computing
The USC-HPCC (High-Performance Computing and Communications) rapidly has become a global leader in research computing and is home to the most powerful supercomputer funded entirely by a private university. The local funding of this resource allows USC researchers unfettered access to this world-class computing environment. USC has a Linux cluster configuration (that is ranked as the 5th fastest academic supercomputer in the USA (spring 2010), and 65th fastest of all supercomputers worldwide, with its’ 1460-node (each with 8 cores), 10-gigabit backbone. The cluster currently has a combined main memory of more than 13 terabytes and a temporary disk storage of more than 400 terabytes. The USC Epigenome Center has a dedicated “condo” of 90 nodes (836 CPU cores), each of which has 16-24 GB of RAM. The USC Epigenome Center maintains 120TB of RAID storage within the Norris Cancer Center for fault-tolerant acquisition and initial processing of sequence data, and 300 TB of high-performance clustered GPFS RAID storage at the HPCC, deployed with a DDN 10ke embedded Gridscaler appliance.
In collaboration with USC’s HSL, USC’s Department of Translational Genomics has mapped a series of bioinformatic tools to department maintained HPC environment that includes 400 compute cores and 600 Tbyte of storage, including software includes Partek™ Genomics Suite, Partek™ Flow, CLC Genomics Workbench™, Ingenuity™, Biobase™, Oncomine™.
Institute of Translational Genomics (Bioinformatics/Computing). The department and Institute have dedicated bioinformatic space for up 6 bioinformaticians within two different areas. These areas are setup with shared computing for interns, and dedicated office space for informatics personnel. Within each room is shared 60” television touchscreen allowing for presentations via Apple TV. Computing comprises a diverse mix of computing and data resources with dedicated condo servers and expandable on demand usage of a larger environment. A series of two Xeon 16 core 256 Gbyte front-end servers provide access to LIMS status, variant reports, and connections to mounting BAMs accessible from a 10Gb internet2 capable switch. These servers also function as datamovers equipped with bbcp/aspera and are capable of 4 simultaneous 1Gbit transfers each. Dedicated computing consists of 480 Xeon cores (Lenovo nx360m5) with access to shared Lustre disks for temporary scratch, and expandable to 1 Petabyte SAN storage through a Dell PowerVault MD3800f system with RAID5 100 Tb racks, and automatic backup-systems provided through an automated Amazon Glacier system.
The Department of Translational Genomics utilizes a custom laboratory information management system (LIMS) developed in-house that supports tracking of all samples that enter the lab, study information, library preparation information (kit used, lot number, manufacturer, protocol used, operator) and sample/library quality control metrics and quantitation before, during, and following library preparation. Information surrounding sequencing of each library is also tracked (sequencer used, flowcell identification number, sequencing reagent and flowcell lot numbers, read lengths, operator, run folder name, run folder location). Following bcl conversion, conversion results are re-imported back into the LIMS to maintain a central location for conversion metrics for individual libraries. This database also communicates directly with our informatics network and in-house analytical pipeline to support seamless initiation of data analysis following each sequencing run.
Clinical Data Management Resources at USC (NCCC): Cancer clinical trials at the USC/Norris Cancer Center (NCCC) are conducted through the Clinical Investigations Support Office (CISO). In operation since 1983, CISO provides assistance to clinical investigators for all stages of protocol development and execution to ensure high quality research. CISO consists of 12 nurse protocol coordinators, 10 CRAs, a specimen and delivery person, a part‑time laboratory technician, a protocol administrator, a quality assurance monitor, a programmer for the protocol database, and 3 secretarial/clerical support staff. CISO is organized to: administratively coordinate clinical research priorities at NCCC; coordinate the development and review of institutional protocols and the conduct of local and national trials; train the nurse protocol coordinators and CRAs at NCCC, and supervise and coordinate their activities in terms of patient and data management for research protocols; ensure high quality research and secure protocol compliance; and to encourage and facilitate interactions between clinical and basic research programs at the cancer center. As part of the CISO operations, the Quality Assurance Committee (QAC) reviews each in-house protocol and selected joint studies, annually in terms of accrual and compliance to the protocol regimen. The number of patients accrued, the target accrual, and the availability of eligible patients are weighed together with observed AERs, reported treatment deviations, and the results of an audit of 2 or 20% of the patients enrolled during the last 12 months (whichever is greater). This audit compares source documentation to research records to confirm the eligibility of each patient, whether treatment was administered according to protocol, and whether side effects and responses were appropriately and accurately recorded. Results of the QAC review and audit are presented to the CIC, along with any recommendations to modify, amend, or close the study.
SC-CTSI. Research Electronic Data Capture (REDCap). Research groups can take a database or survey concept to production level in less than one day. The new instance of REDCap is HIPAA compliant. Input data from anywhere in the world with secure web authentication, data logging, and Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) encryption. Optimized for longitudinal, prospective and/or retrospective studies and multicenter clinical trials provides web-based case report forms, real-time data entry validation (e.g., for data types, range checks), audit trails, and the ability to set up a calendar to schedule and track critical study events such as blood-draws, participant visits. Multi-site access: Projects can be used by researchers from multiple sites and institutions; Advanced question features: Auto-validation, branching logic, and stop actions; Automated "approval" when modifying a project in production; exporting data to Microsoft Excel, SAS, STATA, R, or SPSS for analysis.
Technology & Equipment
Keck Genomics Platform: Within the Institute of Translational Genomics resides the Keck Genomics Platform. Drs. Carpten and Craig established the Keck Genomics Platform to support high throughput Next Generation Sequencing for KSOM faculty. Although KGP is an established USC re-charge center, it operates as both a fee-for-service facility, but also as a collaborative research entity. KGP space is shared within the same open lab environment framework as the Department of Translational Genomics. Major equipment within KGP includes an Illumina NovaSeq™ 6000 Sequencing System, an Illumina MiSeq™, a Covaris high-throughput nucleic acid fragmentation system (LE220) capable of 96 plex fragmentation, an Agilent Bravo ™ automated programmable liquid handling platform, 27 Applied Biosystem thermocyclers, and an additional on-premise computing ensuring redundant capabilities and backups.
Norris Cancer Center Biostatistics Core: Statisticians who are members of the Biostatistics Core are available to provide statistical support to clinical, basic science, and cancer cause and prevention investigators. This support may range from simple advice to participating in the design of the research project, to carrying out aspects of the data management and statistical analysis of a project. The level of support depends on the scale of the project, the support staff available, and the expertise of the investigator. The statisticians in this Core work with members of the Clinical Investigations Support Office (CISO) by participating in the planning, monitoring, and analysis of in-house clinical trials approved by the Clinical Investigations Committee (CIC). They adapt and incorporate innovations in statistical and clinical trial methodology into the design and analysis of cancer research studies.
The USC Norris Molecular Genomics Core: Led by Dr. Carpten, the USC Norris Molecular Genomics Core (MGC) is a service facility that houses state of the art equipment and cutting-edge technologies. Also located within the Norris Research Tower, the MGC is a Norris Comprehensive Cancer Center subsidized core facility, allowing discounts to cancer center members. MGC served as the only data production site for DNA methylation assays for The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA), and one of the largest Illumina single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) and DNA methylation array production sites in the US.
The USC MGC facility houses a number of core genomic profiling systems such as twp Illumina Nextseq500 sequencers, Illumina MiSeq sequencer, and Nanostring nCounter. For microarray support, the laboratory has a full Illumina BeadLab System and a BeadExpress Reader. This system is a production SNP genotyping/expression platform that includes automation equipment (including two Tecan robotic workstations), Laboratory Information Management System (LIMS), BeadArray Readers, BeadStudio data analysis software, hardware and accessories for the generation of millions of genotypes per day or hundreds of thousands of gene expression profiles. All sample tracking uses the Geneus Lab Information Management System (Genologics, Inc.), and the USC Epigenome Center has three programmers which maintain fully automated computational pipelines to process both sequencing and microarray data. The facility also has the following additional equipment available: Bio-Rad Experion, several liquid handling robots including a Qiagen BioRobot 3000 and a Qiagen Rapidplate with Twister II. They also have the Fluidigm BioMark MX/HX real-time analysis system with 4 FC1 thermal cyclers, 8 IFC controllers, 4 HX controllers, 2 MX controllers and 2 Access Array controllers for loading and unloading of array chips for genome partitioning.
Health Sciences Libraries/Other USC Libraries includes the Norris Medical Library and the Wilson Dental Library and includes 168,185 volumes and the Norris Medical Library receives 1,935 current periodicals. In addition, the Information Services Division licenses an additional 250 databases, approximately 2,500 electronic books, and nearly 2,200 electronic journals including over 250 in the biological sciences. The HSL, in cooperation with the Information Services Division, provides all USC users with access to a broad range of print and digital resources. The HSL licenses 14 databases including MEDLINE, EBM Reviews, and other health-related sources through Ovid; 160 electronic books and over 1600 electronic journals through Ovid and through individual publishers. The Norris Medical Library maintains a Web site that provides access to more than 1,700 biomedical information resources. The Norris Medical Library has a Learning Resources Center which offers Internet, database searching, and software application workshops designed to meet the needs of USC health sciences students, faculty, and staff.
